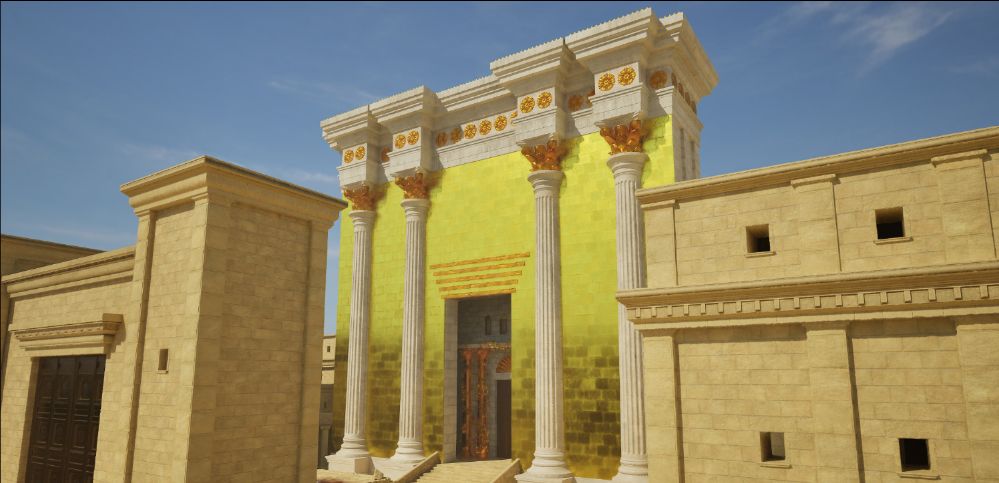
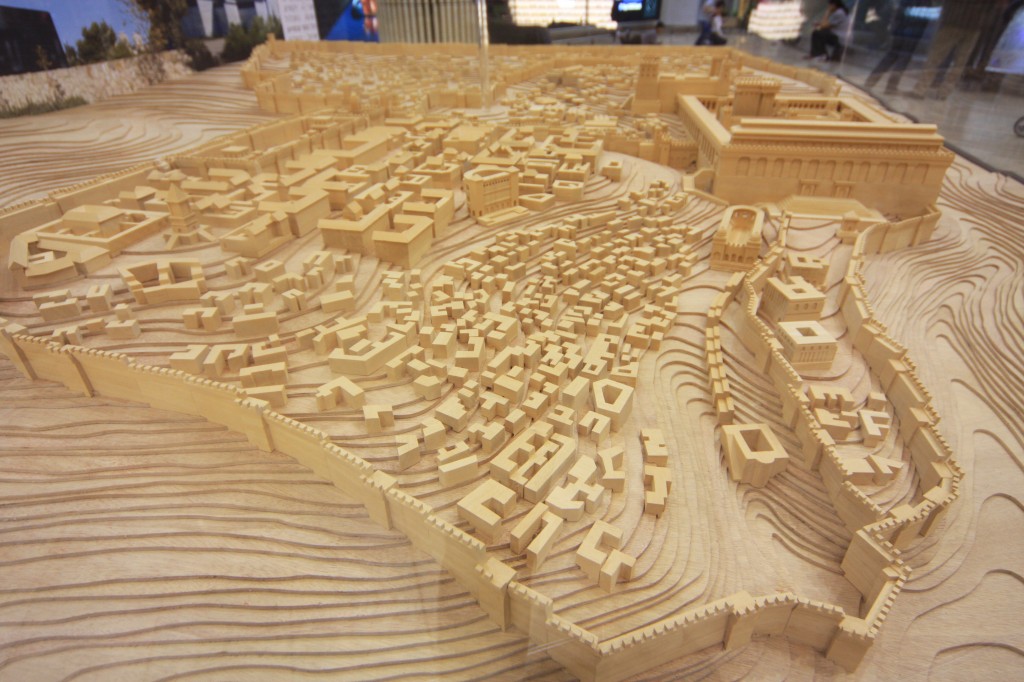
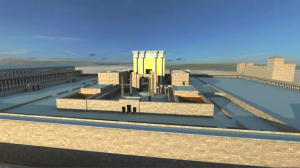
Jeremy Park of bible-scenes.com asked me a while ago if I could help him with his project of developing a 3D video of Herod’s Temple Mount. Last week he wrote the following:
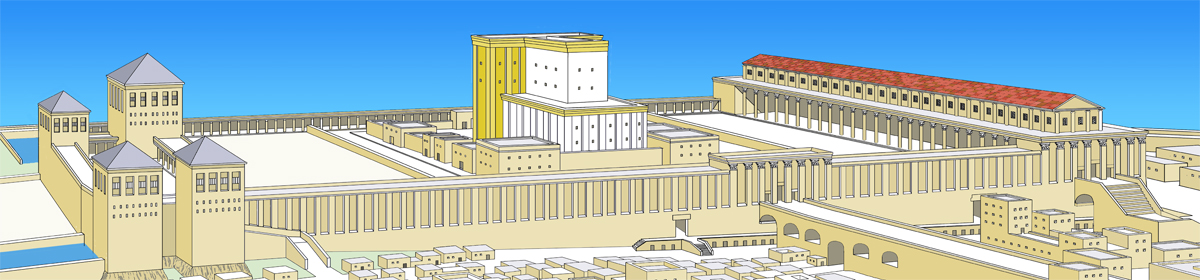
“Shalom to you all. I am so excited to say that after almost two years working on this project it is finally finished; Herod’s Temple Mount. Journey back through time and see what Herod’s Crowning glory the Temple Mount could have looked like two thousand years ago. Places that we can see the remains of today, places like Robinsons Arch and Barclays Gate, Solomon’s Stables and the Western Wall, to name but a few.”
The compilation video can be seen here on YouTube.
“When I made each scene I tried to include people. There were two reasons for this, firstly they gave a sense of proportion and scale as sometimes it is only when you see a person in the shot that you realise just how big some of the structures really are. Secondly, I tried to create a story of each scene where something is happening or has happened. For example, the picture of the two weary travellers on the road in the Kidron valley are obviously talking about the politics of the day:
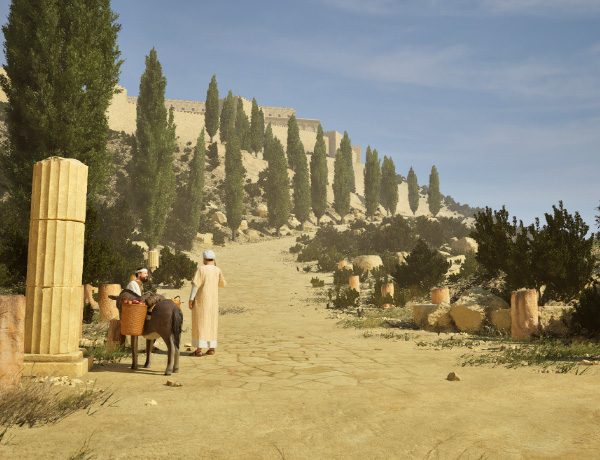

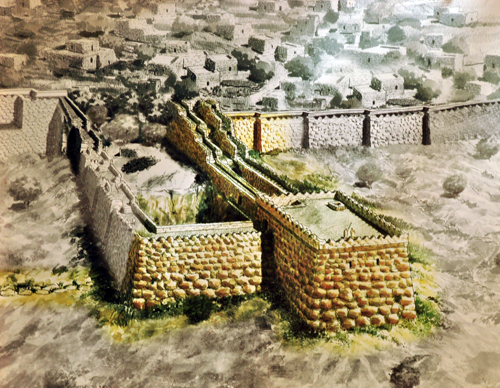
Here are some additional images:
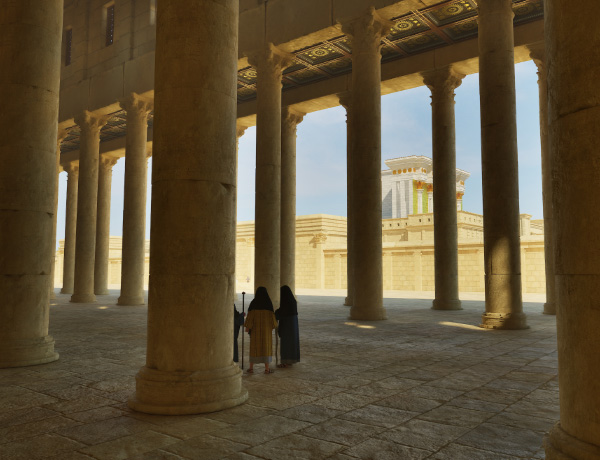
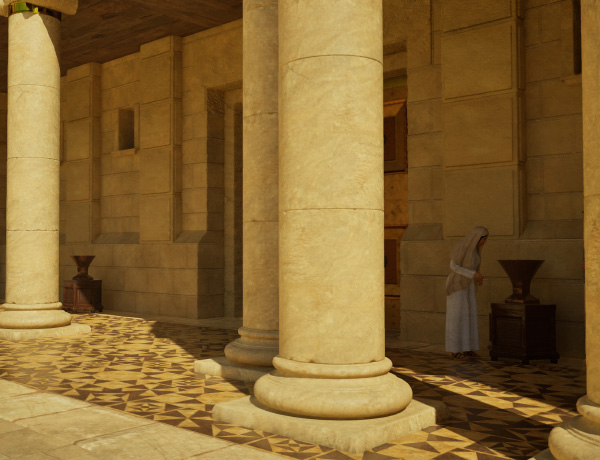
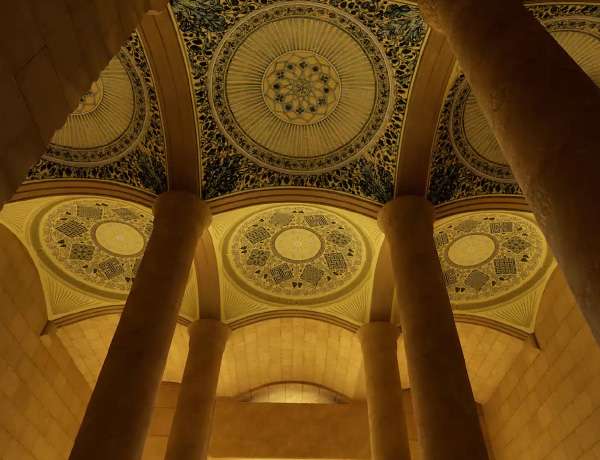
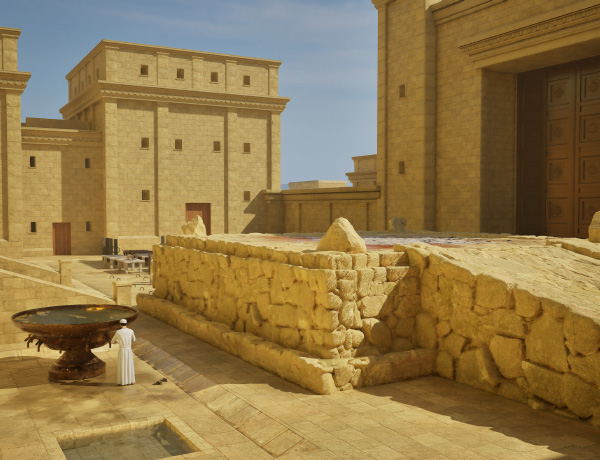





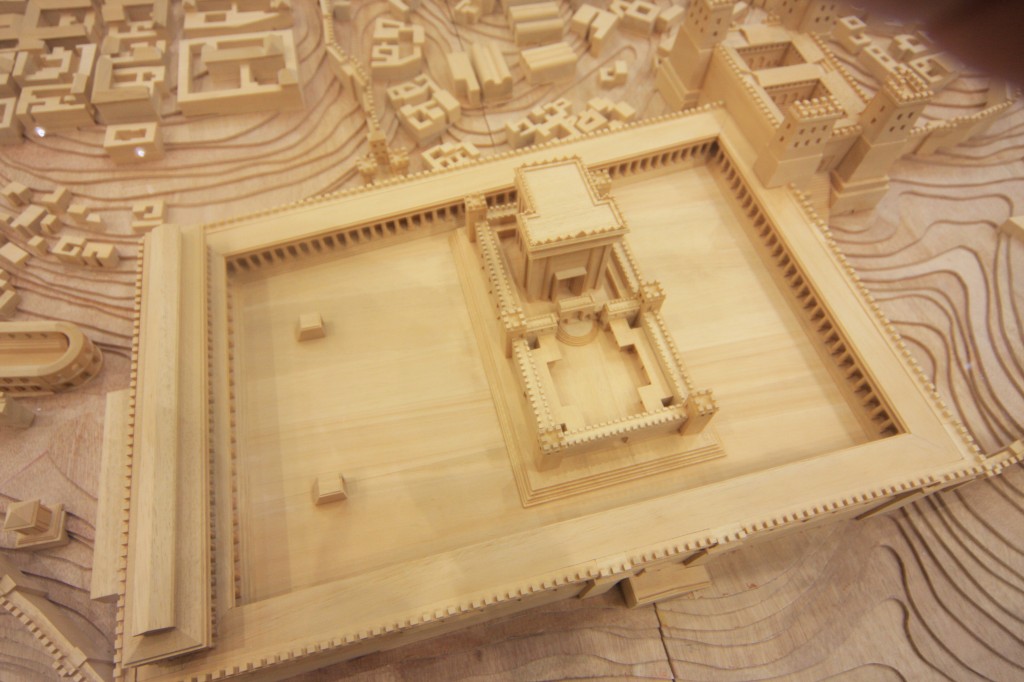
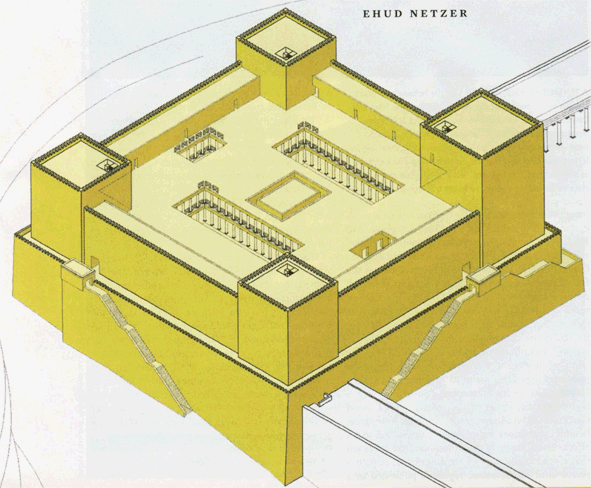
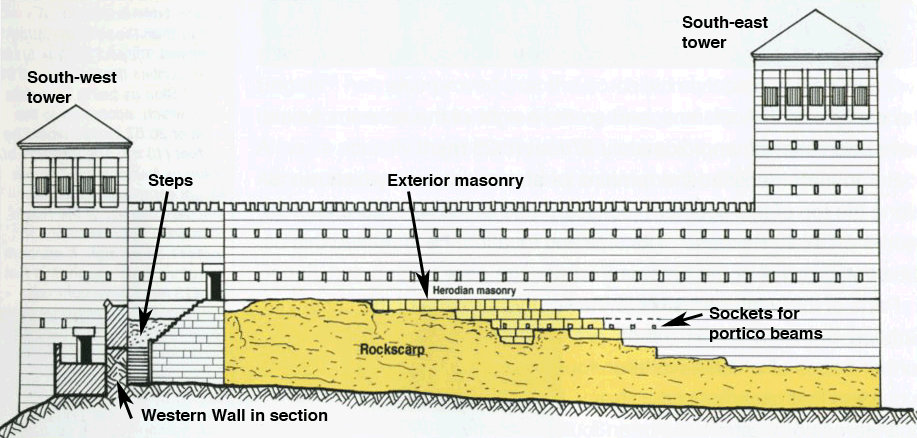
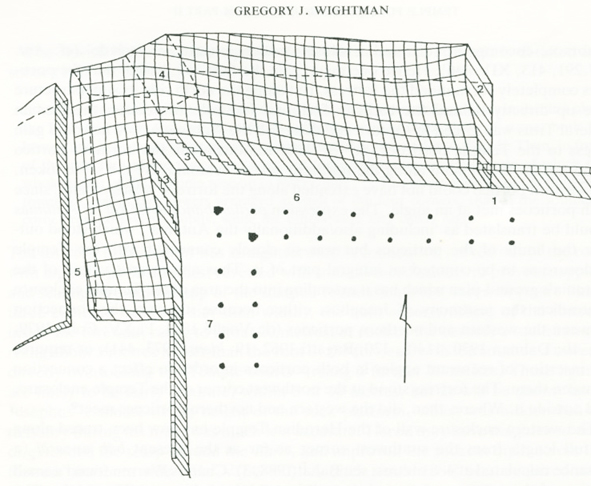
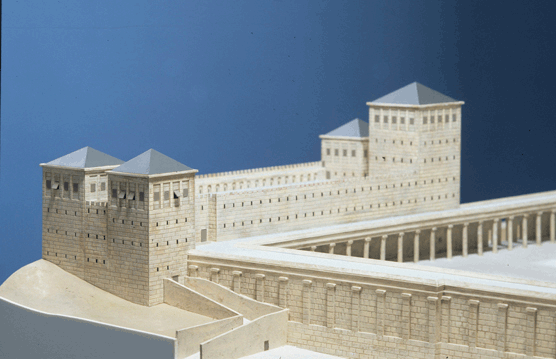
“As most of you are aware by now, I have followed Leen Ritmeyer’s model for this project and if anyone is interested in learning more about the Temple Mount, his book “The Quest” is a gold mine of information.”
“I was fortunate to discover the Ritmeyer Archaeological design Website where I was able to purchase comprehensive plans, elevations, images and information about all aspects of this incredible site that would have been the setting for many Gospel narratives. Without the Ritmeyer resource I don’t think I would have been able to have done justice to the historic and archaeological authenticity of the site.”
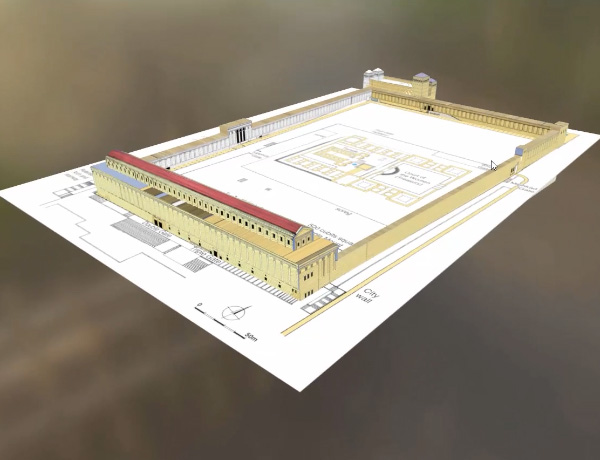
I am probably a little biased when I say that this is the best 3D rendition of the Temple Mount I have seen so far.
Do watch the video and let Jeremy Park know what you think. He would love to hear from you. His HD videos are free to watch and download, but only subscribers can download high-resolution 4K copies:
- The High Definition (HD) videos on this site are free to download and are accessed from the HD download buttons that accompany each scene.
- 4K videos are available to all subscribers.
- When anyone subscribes, an e-mail will be sent out with the necessary password enclosed.
Jeremy’s Bible Scenes is not a separate charity but a branch of his company Park 3D Ltd. Until Bible Scenes can provide him with a sufficient income to work full time on it he has, by neccessity, a day job. He would love to have your support!
What comes next?
“Over the next few days I will be uploading each camera move that you see in this video in HD and 4K to the Bible Scenes Website. As subscribers you will have access to these videos 4 weeks before they are released to the general public (and of course access to them in 4K). I will let you know as soon as the website is updated with the new videos.
After this I will be concentrating on producing individual descriptive videos of most (if not all) of the elements that make up the Temple Mount. For example, there are 18 chambers that surround the Temple itself, all of which serve a different purpose and while I may not be including all of them, I think there is a wealth of information to share regarding them. Then there are the various entrances and gates, the Royal Stoa, the Antonia Fortress and all the other parts that make up this project, all have their own story. I am excited to start producing them and will let you know as soon as they are completed.”
Can’t wait to see all this!